The egg donation process involves several steps, all of which are designed to guarantee the safety and well-being of the egg donor while increasing the chances of success for the intended parents. Understanding the egg donor requirements, and what to expect from the process can help potential donors experience this meaningful experience with confidence.
Step 1: Meeting Egg Donor Requirements
Before starting the egg donation cycle, a potential donor must meet specific egg donor requirements. These requirements are put in place to make sure the egg donor is physically and emotionally ready for the process, and that the donation will be as successful and safe as possible.
Age and Health Criteria
Most egg donation programs require egg donors to be between 19 and 31 years old. This age range is ideal because younger women typically produce healthier eggs. Also, their reproductive health is generally in better condition. This increases the chances of successful fertilization of the eggs. In addition to age, the egg donor must be in good overall health. Factors such as hormone levels and ovarian function are carefully considered to make sure that the donor’s body is capable of responding to the fertility medications required for the donation process.
Another important health factor is the donor’s body mass index (BMI). Most egg donation programs require the egg donor to have a BMI of less than 28. A BMI in this range is considered optimal for fertility, as it ensures the donor’s body is in a healthy weight range. This helps improve the response to hormonal treatments and general reproductive health. A BMI above 28 may lower the chances of successful egg retrieval and increase the chances of complications during the donation process.
Lifestyle and Psychological Evaluation
Besides health factors, egg donors must be in a balanced mental state. A psychological evaluation helps to make sure that the donor is emotionally prepared for the journey and understands the potential impact of the egg donation procedure on both themselves and the intended parents. Lifestyle factors, such as drug and alcohol use, smoking, and general wellness, are also taken into account. Potential donors who lead a healthy lifestyle are more likely to produce a higher number of multiple eggs, which is beneficial for the success of the egg retrieval process.
Step 2: Application and Screening

Once the egg donor meets the basic requirements, the next step is the application and screening process. During this phase, the donor’s medical and emotional readiness are thoroughly evaluated.
Application Process
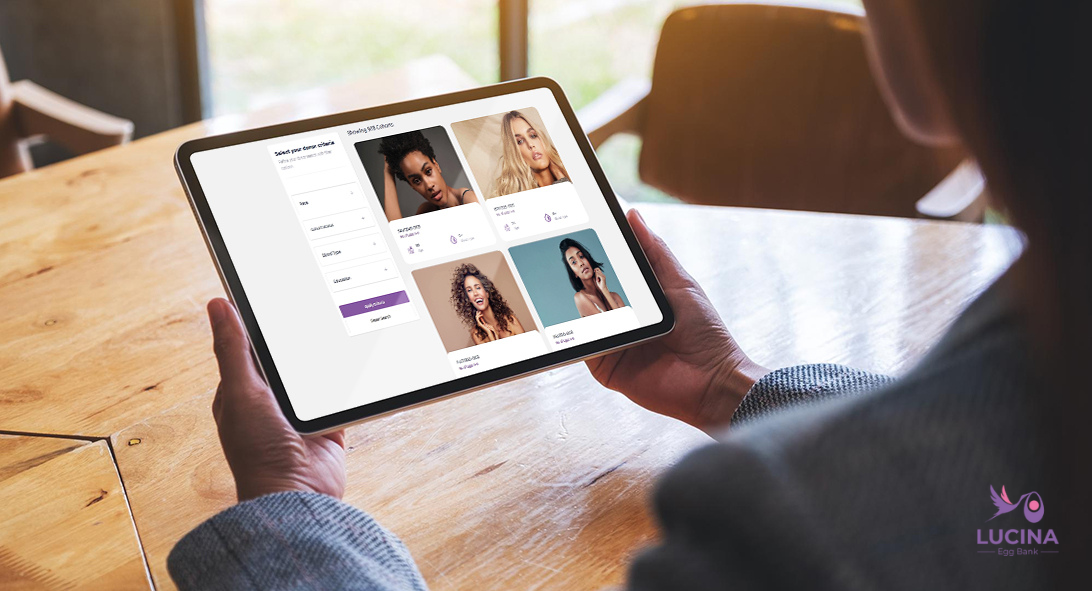
The application process begins with filling out a detailed profile, often through an online application provided by egg banks. This profile includes personal, medical, and family history, which helps the egg bank to check the donor’s eligibility.
Medical and Genetic Screening
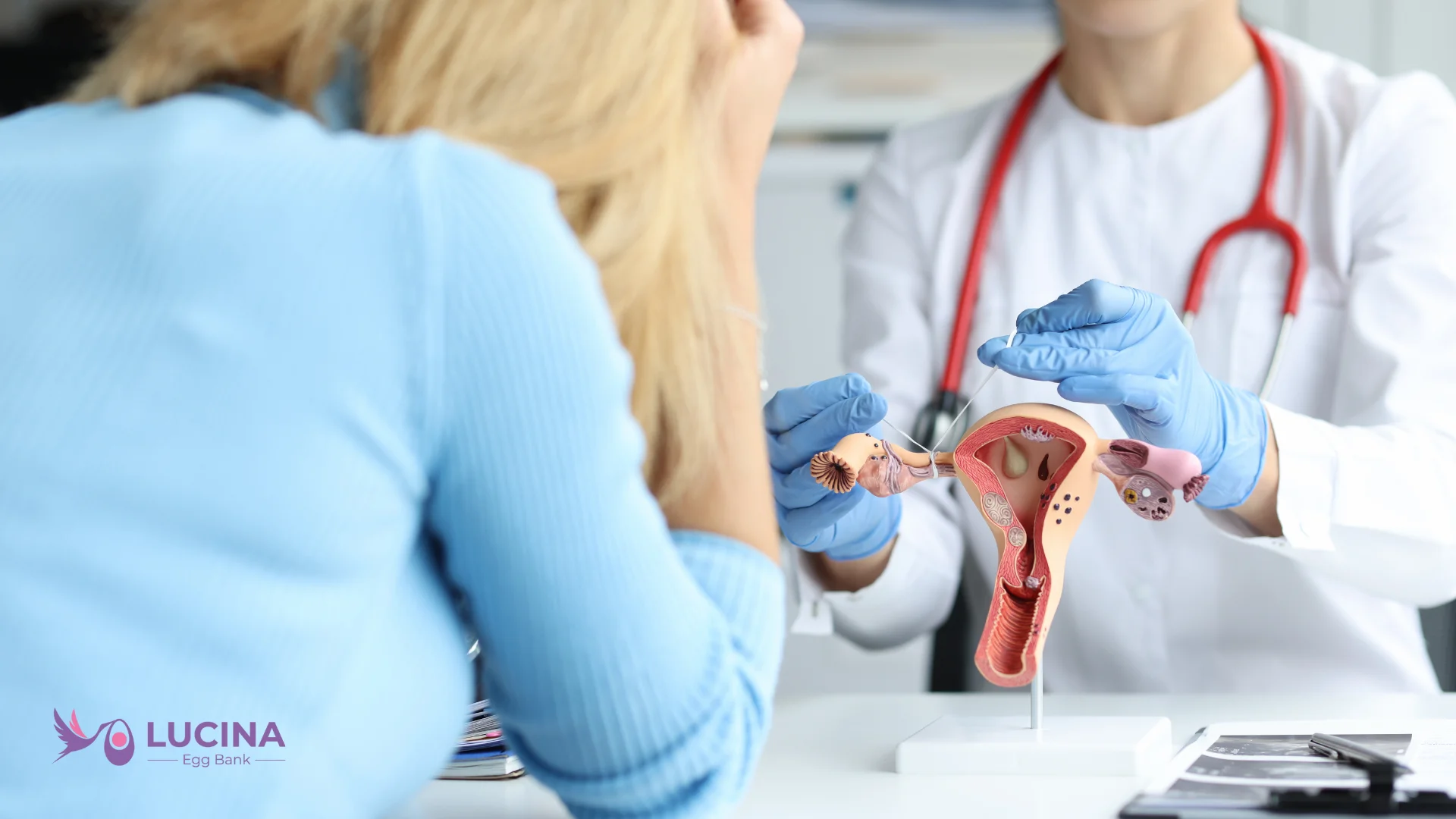
The screening process includes a complete review of the egg donor’s medical history. This involves blood tests to check for any underlying health conditions, such as infections or genetic disorders, that could affect the egg quality. A vaginal ultrasound may also be performed to assess ovarian health, checking for the number and quality of follicles and to make sure the donor’s reproductive system is functioning optimally. Also, the reproductive endocrinologist will check hormone levels to determine how well the donor’s body is prepared to respond to fertility medications.
Psychological Evaluation
A psychological evaluation is also required, as the process of donating eggs can have emotional and psychological impacts. This helps confirm that the donors understand the commitment they are making and that they are comfortable with the idea of their genetic material being used for someone else’s family. Usually, the evaluation is conducted by a licensed professional or specialist who is experienced in reproductive medicine.
Step 3: Compensation and Legal Considerations
The donor will be compensated for their time, effort, and potential risks associated with the donation. Before moving forward with the egg donation process it is important for donors to fully understand both the compensation structure and the legal considerations.
Understanding Contracts and Payments
The compensation for egg donors varies, but it typically includes financial reimbursement for the time, medical procedures, and potential discomfort associated with the donation. The egg donor must also review and sign a legal contract that outlines the rights and responsibilities of both the donor and the fertility clinic. This contract guarantees that the egg donor’s privacy and health are protected while also outlining the financial terms of the donation.
Legal Rights and Responsibilities
It’s important for egg donors to understand their legal rights, particularly regarding the use of their eggs. The contract makes sure that the donor’s genetic material will be used only for the intended purposes and that the donor will not have any parental rights over the resulting children. Egg banks provide legal guidance, and they make sure that the donor is fully informed and protected throughout the egg donation process.
Step 4: Stimulation
Once the egg donor is cleared through the screening process, the next step is ovarian stimulation. This stage involves preparing the donor’s body for the egg retrieval process through hormone treatments.
Hormonal Treatment Explained
During the egg donation procedure, hormone injections are used to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. Normally, a woman’s body releases one egg per cycle, but with the help of fertility medications, the ovaries are prompted to release several eggs simultaneously. This increases the chances of collecting viable eggs for fertilization. The hormonal treatment typically includes hormone injections that stimulate the ovaries to produce eggs at the right time.
Monitoring During This Phase
The donor will be closely monitored throughout this phase with regular blood tests and ultrasounds to track the body’s response to the hormones. These tests help adjust the dosage of fertility medications if necessary, making sure the donor’s ovaries are producing multiple healthy eggs for retrieval. This monitoring helps minimize risks such as ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), a rare but possible side effect of ovarian stimulation.
Step 5: The Egg Retrieval Process
After several days of hormone treatment, the donor’s eggs are ready to be collected. The egg retrieval process is the main step in the egg donation cycle.
Preparation for the Procedure
Before the procedure, the egg donor undergoes a final set of instructions from the medical team to make sure they are ready for the next steps. This preparation may include a trigger shot, a final injection administered about 36 hours before the retrieval to help the eggs reach full maturity. The donor will be given instructions on when to stop eating and drinking to guarantee safety during sedation. Since the egg retrieval procedure is typically performed under light sedation, donors are advised to arrange for someone to accompany them to the clinic for support and transportation afterward.
The Egg Retrieval: What to Expect
The egg retrieval is a minimally invasive and relatively quick procedure, usually completed within 20-30 minutes. During the process, the reproductive endocrinologist uses a vaginal ultrasound to locate the ovaries and guide a specialized needle to collect the mature eggs. This precise and delicate process is conducted in a controlled, sterile environment to provide safety and guarantee the best quality of eggs. After the retrieval, the eggs are carefully inspected and prepared for fertilization in the lab, marking a critical step in helping intended parents on their journey to building a family.
Step 6: Post-Retrieval Care

After the egg retrieval process, the donor will need to rest and recover. Though the procedure is minimally invasive, it can still cause some discomfort or mild side effects.
Recovery and Possible Side Effects
Most egg donors experience some cramping or bloating after the procedure. These side effects typically subside within a few days. However, it’s important for the donor to take time to recover and follow any medical advice provided by the clinic. Regular follow-up appointments are scheduled to make sure the donor’s body returns to normal and that there aren´t complications from the egg retrieval.
Follow-Up Appointments
Follow-up appointments are essential to make sure the egg donor’s recovery is progressing as expected. These appointments involve blood tests to monitor hormone levels and confirm that the body is returning to its pre-donation state.
Throughout this phase, egg donors are closely followed up on how they feel, both physically and emotionally. Most egg banks have specialized staff dedicated to maintaining permanent contact with donors, offering support and guidance at every step. These professionals make sure that any questions or concerns are addressed promptly, creating a reassuring and supportive experience for donors during their recovery period.
The egg donation process involves multiple stages, including medical screening, egg retrieval, hormonal stimulation, and recovery. Understanding the egg donation process can help potential donors make informed decisions and confidently experience this life-changing journey. With the right support, egg donation can be a meaningful and life-changing experience for donors, offering them the chance to help families achieve their dream of parenthood.